Millennials Have More Student Debt: Unveiling the Burden
Millennials carry a larger student debt burden than previous generations. This demographic faces unique financial challenges as a result.
Millennials, often referred to as Generation Y, have been significantly impacted by the rising costs of higher education. As this group pursued college degrees, they encountered steep tuition increases, resulting in an unprecedented level of student loan debt. Consequently, this financial strain has altered the traditional milestones associated with adulthood, such as home ownership and starting a family.
Understanding the implications of this economic burden is crucial for both millennials and policy makers. Addressing these challenges requires insight into the socioeconomic factors contributing to the student debt crisis. The conversation surrounding this issue is vital as it influences the financial well-being and future prospects of an entire generation.

Credit: www.ced.org
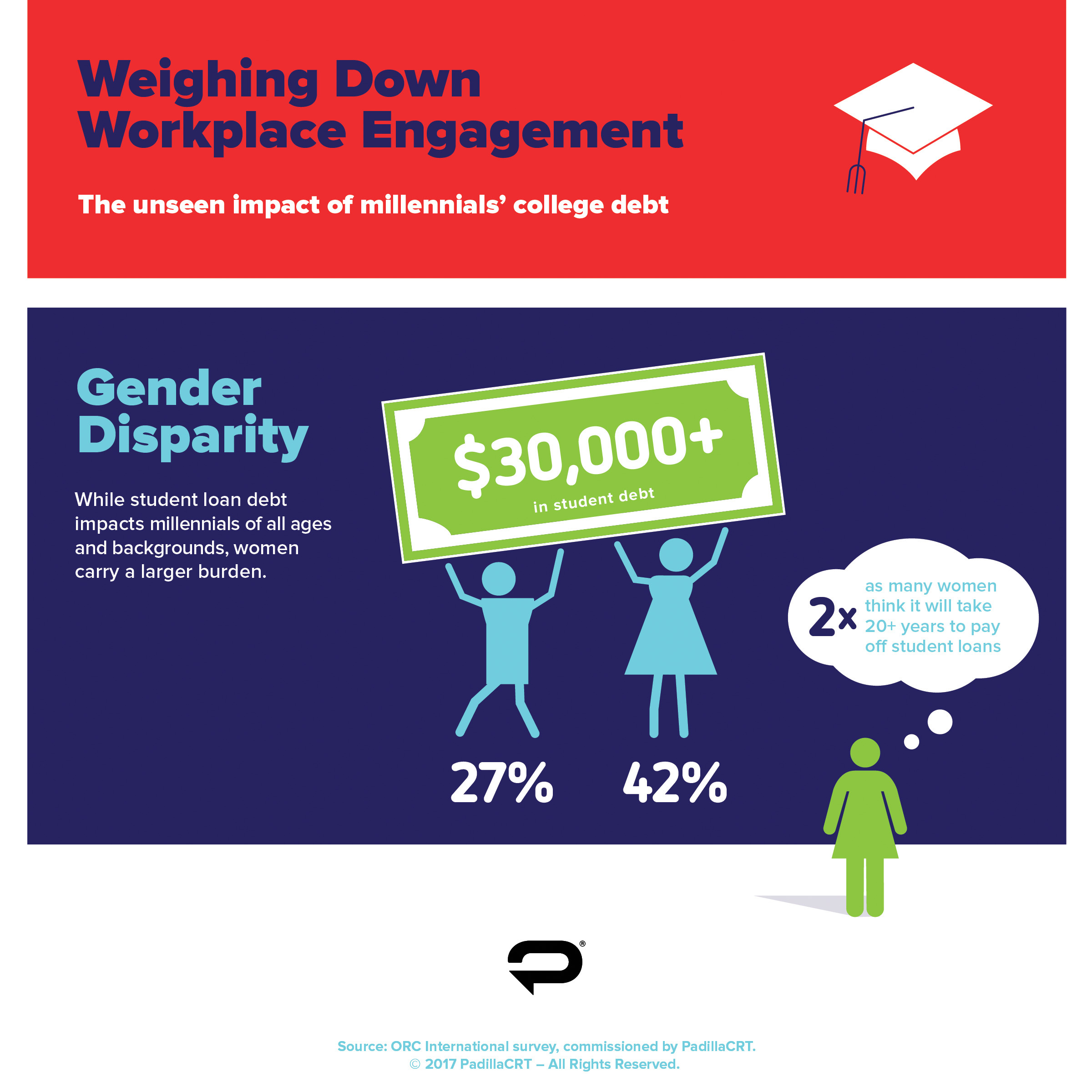
The Student Debt Snapshot: Millennials At A Glance
Understanding the financial hurdles millennials face is essential in today’s economy. Student debt is a significant burden for this generation. Let’s examine how this student debt crisis pertains particularly to millennials.
Skyrocketing Costs Of Higher Education
College tuition has soared over the past few decades, surpassing inflation and family income growth. This rise makes affording college without loans tough for many. Schools list their rising operational costs as a key reason for these increases. Use of advanced technology and the need for more specialized staff add to this. As a result, millennials have had to shoulder heavier financial loads to pursue their education ambitions. Tuition spikes have pushed them towards larger student loans.
Comparing Generational Debt Loads
Student debt is not new, but millennials bear its brunt more than previous generations. A look at the numbers tells the story. Statistics show millennials have more student debt than Baby Boomers or Gen Xers had at their age. This is due to expensive tuition and the increasing necessity of a college degree in the job market.
- Baby Boomers: Often paid their way through school or had minimal loans.
- Gen Xers: Faced increased tuition, starting the upward trend in student debt.
- Millennials: Confront the peak of this trend, with student debt figures skyrocketing.
Here’s a simple comparison table that highlights the generational differences in student debt loads:
| Generation | Average Debt at Graduation | Percentage with Student Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Baby Boomers | $10,000 | 30% |
| Gen Xers | $20,000 | 50% |
| Millennials | $30,000+ | 70% |
This table vividly highlights the growth in both the amount owed and the number of individuals in debt across generations. Millennials top this unfortunate chart, signaling a need for solutions and support to manage this growing issue.
Why Millennials Bear The Brunt
Millennials face unprecedented student debt levels, eclipsing previous generations. The reasons for this financial burden are multifaceted, with economic events and educational policies playing critical roles. Understanding the causes of this debt crisis is essential for crafting solutions.
Economic Context: Recession And Recovery
The millennial generation entered a challenging job market. The Great Recession’s effects, with high unemployment rates, made it difficult to repay loans. Lower earnings limited their financial growth significantly.
- 2008 financial crisis led to scarce job opportunities
- Graduates faced underemployment, disrupting repayment plans
- Delay in career establishment pushed financial milestones back
Shifts In College Funding Models
At the same time, a shift in funding for higher education burdened students more. State funding cuts forced colleges to hike tuition fees. This required students to rely heavily on loans.
| Year | State Funding Change | Tuition Fee Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-2000 | Higher | Lower |
| Post-2000 | Lower | Higher |
- State support reduction for public institutions
- Greater portion of cost shifted to students
- Student loans became a necessity for many
Impact On Life Milestones
Moving through life’s major milestones feels like a tough climb for millennials wrestling with student debt. More than previous generations, this cohort faces unique challenges that affect their long-term financial stability and goals. Let’s explore how heavy student loans are reshaping the life achievements once taken for granted by earlier generations.
Homeownership And Investment Delays
Dreams of owning a home often stay just that, dreams, for those buried under student loans. High monthly payments limit their ability to save for a down payment. Credit scores can also suffer, making mortgages less accessible or more costly.
- Millennials are buying homes later than their parents did.
- Student debt leads to renting longer and delaying investment in property.
- Smaller budgets mean fewer choices in an already competitive housing market.
Retirement Savings: A Distant Dream?
Student debt doesn’t just delay the now; it pushes retirement planning to the back burner. Immediate debt payments often take precedence over long-term savings. This has real consequences:
| Without Debt | With Student Debt |
|---|---|
| Earlier and more retirement savings | Retirement savings start later and grow slower |
| Potential for compound interest growth | Lost compounding years reduce total retirement funds |
Regular contributions to a retirement plan might seem a luxury when facing steep loan payments. Thus, millennials often see retirement savings as a distant dream, not a present priority.

Credit: whyy.org
Exploring Solutions And Forgiveness Programs
Millennials face a rising tide of student debt. This burden affects their financial freedom. Many seek help and hope through solutions and forgiveness programs. Such programs promise to ease the weight of educational loans. Our focus now turns to the various pathways for managing and potentially reducing student debt.
Policy Proposals And Political Debates
Lawmakers are engaging in debates to find ways to support the millennial generation. Proposals range from income-based repayment plans to loan forgiveness.
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Adjustments to monthly payments based on income.
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness: Debt relief for those serving in public roles.
- Student Debt Cancellation: Proposals to wipe out certain amounts of student debt.
These policy propositions aim to provide relief and foster economic growth. The debates emphasize fair and accessible education for all.
Private Sector Initiatives And Employer Assistance
Businesses recognize the need to support employees with student loans. The private sector introduces creative solutions.
- Loan Repayment Benefits: Companies offer to pay part of their employees’ student loans.
- Refinancing Options: Partnerships with financial institutions for better loan terms.
- Financial Wellness Programs: Education and resources to manage debt effectively.
These measures benefit both employees and employers. Companies attract talent while individuals gain financial relief.
Personal Finance Strategies For Coping
Personal Finance Strategies for Coping with student debt can help Millennials manage their financial obligations more efficiently. Student loans are a significant burden, but with the right approach, they can be tackled head-on. Below are key strategies tailored to aid in establising control over your finances.
Budgeting Around Loan Repayment
Creating a budget is fundamental for managing student loans. This plan allocates your income towards essentials, savings, and debt repayment. Consider these steps for a balanced budget:
- Track every expense to understand where your money goes.
- Categorize expenses and identify areas for cost-cutting.
- Prioritize loan payments to avoid additional interest.
- Set aside an emergency fund to prevent derailing your repayment plan.
Refinancing Options And Resources
Refinancing can provide relief by lowering interest rates or adjusting payment terms. Below are resources to explore:
| Resource | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lender Websites | Offer detailed info on loan products | Better rates and terms |
| Financial Advisors | Provide personalized advice | Strategic planning |
| Government Programs | Options for federal loan holders | Potential forgiveness eligibility |
Before refinancing, consider the impact on federal loan protections, such as forgiveness and income-driven repayment plans. Always compare offers from multiple lenders for the best deal.

Credit: www.bankrate.com
The Future Of Education Financing
Millennials grapple with hefty student loans, unlike past generations. The pursuit of higher education often leads to a mountain of debt. With tuition fees soaring, students and families seek new solutions. This situation ignites a profound transformation in how we finance education. Several innovative approaches are emerging to tackle this financial challenge. Let’s dive into the trendsetting strategies shaping the future of education financing.
Innovative Funding Models
- Income Share Agreements (ISAs): Students pay back a portion of their income after graduation, rather than upfront tuition.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like GoFundMe support students in raising funds for their education from a broader community.
- Scholarship-Matching Platforms: Tools such as Scholly connect students with relevant scholarships, reducing reliance on loans.
- Employer Sponsorship: Companies invest in their employees’ education, hoping for a return through enhanced skills and loyalty.
College Alternatives
Some students sidestep traditional colleges entirely. They choose paths less burdened by debt. Vocational schools, coding bootcamps, and online courses offer practical skills. These alternatives provide quicker, more affordable routes to employment. For example:
| Alternative | Duration | Cost Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Coding Bootcamps | 3-12 months | Less than traditional four-year degree |
| Online Courses | Varies | Often pay-per-course |
| Vocational Schools | 1-2 years | Typically lower than universities |
The Role Of Technology In Reducing Costs
Digital innovations offer cost-cutting benefits. E-textbooks save on print and distribution costs. Virtual classrooms eliminate the need for physical space. AI-driven advising tools streamline course selection. Tech-forward solutions like these make education more accessible. They also lead to substantial savings for students.
- Online course platforms reduce or eliminate campus expenses.
- Open-source materials provide free educational content.
- Technology grants target underserved populations.
Together, these methods present promising avenues. They alleviate the financial burden of pursuing higher education.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Millennials Have More Student Debt
Why Do Millennials Have High Student Debt?
Millennials often face substantial student debt due to rising tuition costs. They enrolled in higher education during a time of increased college expenses, without a proportional rise in family income or financial aid.
What’s The Average Student Debt For Millennials?
On average, Millennials carry approximately $30,000 in student debt. This varies based on the level of education obtained and the institution attended. Graduate degrees often result in significantly higher debt levels.
How Does Student Debt Affect Millennials’ Lives?
Student debt impacts Millennials’ financial decisions, delaying milestones like home ownership, marriage, and starting a family. It often necessitates budgeting for long-term loan repayment, affecting their savings and investment opportunities.
Can Millennials Get Student Debt Forgiveness?
Some Millennials may qualify for student debt forgiveness through programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness. They must meet specific criteria, such as working in public service and making 120 qualifying payments, to receive forgiveness.
Conclusion
Navigating the financial challenges of higher education is tougher for millennials than ever before. With student debt reaching unprecedented levels, effective solutions and enhanced support systems are essential. It’s critical we address these economic hurdles to unlock the potential within this generation.
Let’s empower them for a brighter, more sustainable future.







