Statistics About Millennials With Student Loan Debt: Eye-Opening Trends
As of recent studies, nearly 45 million millennials carry student loan debt. The average balance exceeds $30,000 per borrower, indicating significant financial strain.
Navigating the financial landscape of today’s economy, millennials with student loan debt face a unique set of challenges. Saddled with significant borrowing for education, this generation’s financial freedom is often delayed, impacting their ability to invest, purchase homes, and make other large economic decisions.
The burden of repayment looms large, with many young adults dedicating a substantial portion of their income to servicing this debt. Understanding these statistics is crucial not only for policy makers and financial institutions but also for millennials themselves as they strategize their financial futures. Debt management and financial literacy become paramount in addressing the issues associated with such widespread indebtedness among millennials.
Credit: thefinancialbrand.com
Millennials And Student Debt: A Financial Snapshot
Millennials and Student Debt: A Financial Snapshot provides a compelling view into the financial burdens that this generation faces. Student loans are not just a footnote in millennial finances; they are a significant chapter in their economic story. From defining their budgeting strategies to impacting long-term saving plans, student debt continues to shape the financial landscape for many young adults.
Average Debt Load For Millennial Graduates
On average, millennial college graduates shoulder a substantial amount of debt. This financial weight often defines their early professional years. Bold decisions like buying a home get pushed back. To paint a clearer picture:
- Millennial bachelor’s degree holders average about $30,000 in debt.
- Those with advanced degrees often surpass $50,000.
- Repayment timelines can extend over decades, influencing life choices and financial freedom.
Comparisons With Previous Generations
The student debt landscape has changed dramatically over the years. To contrast:
| Generation | Average Student Debt at Graduation |
|---|---|
| Millennials | $30,000+ |
| Generation X | About $20,000 |
| Baby Boomers | Less than $10,000 |
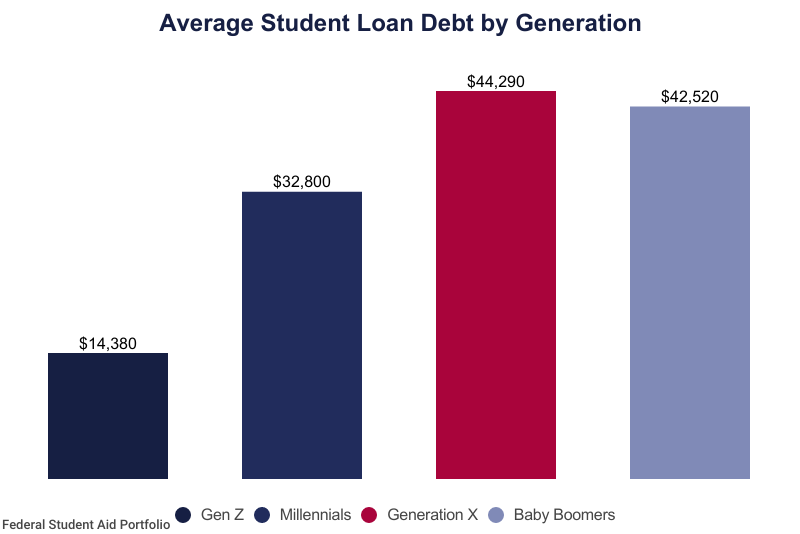
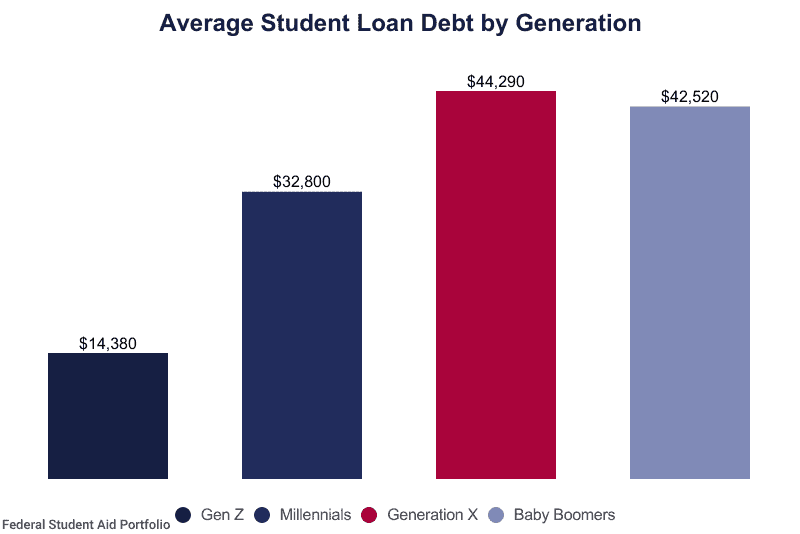
Millennials have taken on nearly twice the student debt as Generation X and three times that of Baby Boomers. Factors include tuition hikes and the increased demand for higher education.
Contributing Factors To Rising Student Debt
The burden of student loan debt among millennials is a growing concern. This weighty financial strain didn’t materialize out of thin air. Instead, various factors combined to inflate this bubble of debt. Understanding these causes is crucial in addressing the issue. Today, let’s shed light on some key elements contributing to soaring student debt levels.
Tuition Inflation Over The Years
Tuition costs have skyrocketed, far outpacing inflation and family income growth. Let’s review the numbers:
- Public four-year institutions: Tuition and fees have nearly tripled since the 1980s.
- Private nonprofit four-year colleges: Costs have doubled within the same period.
Data reveals that college affordability is a relic of the past, leaving millennials scrambling to cover the gap.
Shifts In Federal And State Education Funding
Another major player is the reduction in government contributions toward higher education. Funding cuts have transferred costs from the states to the students. A closer look:
| Year | Federal Funding | State Funding | Student Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990s | Higher | More robust | Lower |
| 2020s | Lower | Reduced | Higher |
This juxtaposition highlights the increased reliance on student loans to pursue higher education.
Private Loans And Interest Rates
Private student loans have painted a complex financial landscape. Unlike federal loans, they come with variable interest rates. These can escalate, piling on additional debt. Key insights:
- Private loan interest rates can surpass 13%.
- Federal loans limit interest rates and offer fixed options.
- Private loans lack income-driven repayment plans.
The result: an unpredictable burden. Many millennials find themselves trapped in a cycle of high-cost debt that outpaces their earning potential.
The Impact Of Student Debt On Millennial Lives
Student loan debt is a significant burden for many millennials, affecting various aspects of their lives. From altering life milestones to influencing career paths, the repercussions are profound and enduring.
Delayed Milestones: Homeownership And Marriage
High levels of debt often lead millennials to postpone significant life events. Homeownership and marriage rates have seen notable declines among this demographic, as financial obligations take centre stage.
- Homeownership delayed due to the inability to save for a down payment.
- Concerns over debt contributing to a reluctance to marry and start families.
Effects On Career Choices And Entrepreneurship
Millennials with heavy student loan debt tend to choose jobs based on salary prospects rather than passion. This need for financial security also impacts their willingness to take entrepreneurial risks.
- Ideal career paths often sidelined for those with better financial returns.
- Starting a business viewed as too risky when prioritizing loan repayment.
Mental Health Concerns And Financial Stress
Student loan debt is not just a financial problem; it also affects millennial mental health. The constant stress of managing debt can lead to anxiety, depression, and reduced overall well-being.
- Financial stress correlated with increased rates of anxiety and depression.
- Debt-induced stress can lead to long-term health effects.
Geographic Disparities In Student Loan Debt
Geographic Disparities in Student Loan Debt reveal a complex picture of the financial challenges facing Millennials across the United States. Factors such as state policies, cost of living, and the local job market create a varied landscape of student loan burdens. This section delves into the differences in debt levels among states and cities, and contrasts the debt trends between rural and urban Millennial residents.
State And City Differences In Average Debt
Millennials in different states and cities see a wide range in average student loan debt. States with high costs of living tend to show higher debt levels. Cities with a concentration of higher education institutions might result in elevated local averages. Here are some striking trends:
- New York and California often lead in high student loan figures.
- Smaller cities may exhibit lower debt due to less expensive colleges.
- States with generous aid programs might show decreased average debts.
| State/City | Average Debt |
|---|---|
| New York | $30,000 |
| Utah | $18,838 |
| Los Angeles | $25,000 |
Rural Vs. Urban Millennial Debt Trends
Millennials in rural areas face a different student loan landscape than their urban counterparts. Let’s explore some key points:
- Rural Millennials might attend local colleges leading to potentially lower debts.
- Urban Millennials often have access to higher salaries, aiding faster debt repayment.
- Cost of living differences can impact the ability to pay off loans.
Rural and urban disparities underscore the need for tailored debt solutions. Understanding these complexities helps stakeholders address the student loan crisis effectively.
Efforts To Mitigate Student Loan Burdens
The weight of student loan debt has pressed down on millennials for years. Innovative solutions and programs aim to lighten this load. These strategies foster hope and provide pathways to financial freedom. Let’s explore the efforts making a difference today.
Loan Forgiveness Programs: Successes And Drawbacks
Loan forgiveness programs offer significant relief to eligible borrowers. These initiatives can erase portions or entire debts. Yet, each comes with specific conditions and results vary.
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Aids those working in public service. Yet, bureaucratic hurdles often complicate qualification.
- Income-Driven Repayment Forgiveness: Caps repayments based on income. It extends the payment period but may result in a tax bill on forgiven amounts.
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness: Supports educators in low-income schools. Paperwork and stringent criteria can challenge applicants.
Success reflects in the beneficiaries freed from debt. The drawbacks center on the complex application processes and qualifying stipulations that exclude many.
Recent Legislation And Policy Changes
In recent years, new laws and policy updates have been introduced. These aim to simplify repayment and provide more forgiveness options.
- Legislators have expanded repayment options and adjusted interest rates.
- New reforms target the mechanics of forgiveness, aiming to automate and streamline the process.
- Emergency relief measures, like loan forbearance during crises, grant temporary reprieve.
Borrowers must stay informed on changes to capitalize on opportunities for relief.
Educational And Financial Advice For Current Students
Preventive measures are key for current and future students. It’s important to balance ambition with financial reality.
| Strategy | Details | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Research Scholarships | Explore grants and scholarships early. | Reduces borrowing needs. |
| Budgeting | Manage expenses and save money. | Lessens financial strain. |
| Part-time Employment | Consider work-study or part-time jobs. | Offers income to offset costs. |
Informed choices lead to manageable loan obligations. Early financial literacy empowers students to make savvy decisions pre-and post-graduation.
Credit: educationdata.org
The Future Outlook For Millennial Debt
Understanding the financial path ahead for millennials with student loan debt is crucial. It shapes their personal economic future and impacts the broader economy. Let’s explore important facets of this issue.
Projections For Debt Repayment Timelines
- Many millennials face decades of payments.
- Recent grads may spend 20+ years repaying loans.
- Differences in income affect repayment speed.
- Loan forgiveness plans alter timelines.
Timelines extend as new grads join the debt pool. Some may retire before clearing their debt.
The Prospects Of Reform In Higher Education Finance
Changes in higher education funding could ease the debt burden.
- Legislation might reduce interest rates.
- Income-driven repayment plans can adapt.
- Tuition cuts could lower future loans.
Reform aims to improve affordability for future students, potentially easing the millennial debt crisis.
Long-term Economic Implications For The Millennial Generation
| Impact Area | Effect |
|---|---|
| Homeownership | Delays in purchasing homes |
| Savings | Lower savings rates |
| Retirement | Postponed retirement plans |
Sustained debt restricts economic growth opportunities. It limits millennials’ ability to invest in assets like homes.

Credit: www.opploans.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Statistics About Millennials With Student Loan Debt
What Percentage Of Millennials Have Student Loans?
Millennials are significantly affected by student debt, with approximately 1 in 3 adults under the age of 30 holding student loan debt, according to the Pew Research Center.
How Much Student Loan Debt Do Millennials Carry On Average?
On average, millennials carry around $30,000 in student loan debt. This figure can vary greatly depending on the level of education and institution attended.
Are Student Loans Impacting Millennials’ Homeownership?
Yes, student loan debt is delaying homeownership for millennials. Studies suggest that for every 10% increase in student loan debt, homeownership is postponed by about one to two years.
Why Are Millennials Struggling With Student Loan Debt?
Millennials struggle with student loan debt due to rising college tuitions, the economic downturn during their career entry, and stagnant wages that have not kept up with living costs.
Conclusion
Understanding the financial pressures millennials face with student loan debt is critical. These statistics offer insight into the issue’s scope and impact. As we seek solutions, consider the weight of these numbers. Let’s move toward a future where education is a gateway to opportunity, not a burden of debt.







