Millennial Student Loan Debt Statistics: Alarming Trends
Millennial student loan debt in the United States has reached an average of $30,000 per borrower. This figure encapsulates the financial burden on the generation.
Navigating the complexities of millennial student loan debt requires a clear understanding of the current landscape. Skyrocketing tuition costs coupled with competitive job markets have led many millennials to bear the weight of substantial educational loans. This financial strain impacts their ability to purchase homes, save for retirement, or invest in their futures.
As the student debt crisis deepens, its ramifications extend beyond individual borrowers, influencing economic trends and consumer behavior. Our insight into these statistics shines a light on the challenges faced by a generation striving for success amidst a backdrop of persistent debt. By examining these trends, we can better understand the socioeconomic factors contributing to the millennial dilemma and explore potential pathways to alleviate this widespread fiscal predicament.
The Rise Of Student Loan Debt Among Millennials
The Rise of Student Loan Debt Among Millennials has become a pressing issue in today’s financial landscape. With college costs escalating at an unprecedented rate, many young adults find themselves burdened by hefty loans as they step out into the real world. Understanding why this generation faces such high levels of debt is crucial in addressing the crisis.
Factors Contribiting To Increased Borrowing
Several key elements have led to the growth of student loan debt among millennials:
- Skyrocketing College Fees: Tuition costs have risen sharply, outpacing inflation.
- Changing Economic Climate: Shrinking state funding adds to the financial strain on institutions and students alike.
- Wage Stagnation: Slow growth in real wages has not kept up with the cost of higher education.
- Shift in Attitude: There is an increased emphasis on obtaining a college degree for career success.
Comparative Analysis: Then And Now
Delving into the past versus present scenarios illuminates the stark contrast:
| Aspect | Then (Gen Xers) | Now (Millennials) |
|---|---|---|
| Average Tuition Cost | More affordable, seldom requiring loans | High, often demanding large loans |
| State Funding | Better supported by government programs | Reduced, leading to greater personal burden |
| Wages Post-Graduation | Consistently increased in proportion to cost of living | Stagnated, making loan repayment challenging |
Such a comparison clearly exhibits why millennials confront more significant financial hurdles than the previous generation, compounding their student loan debts.

Credit: www.americanbanker.com
Impact On Millennial Financial Health
Student loan debt casts a long shadow on Millennials. This debt affects their financial stability. It often leads to the delay in key life events. Buying a house or saving for retirement can wait. We will explore how this debt impacts Millennials in more detail below.
Delay In Major Life Milestones
Heavy student loan debts delay major life milestones for many Millennials. Home ownership, marriage, and starting a family are often pushed back. See the major shifts below:
- Home Ownership: High debt-to-income ratios impede mortgage approvals.
- Marriage: Financial strain can postpone wedding plans.
- Family Planning: The cost of childcare combined with student debt limits family growth.
Credit Score And Purchasing Power
Student loans can help build credit if managed well. Yet, missed payments damage credit scores. See how credit health influences purchasing power:
- Credit Score: A lower score results from missed payments, affecting future borrowing.
- Purchasing Power: With weakened credit, buying on credit or getting loans becomes harder.
Mental Health Repercussions
The burden of student debt takes a toll on mental health. Stress and anxiety are common among indebted Millennials. The key concerns include:
- Stress: Constant worry about repaying debt leads to chronic stress.
- Anxiety: Uncertainty about financial independence fuels anxiety.
- Depression: Ongoing financial struggles can contribute to depression.
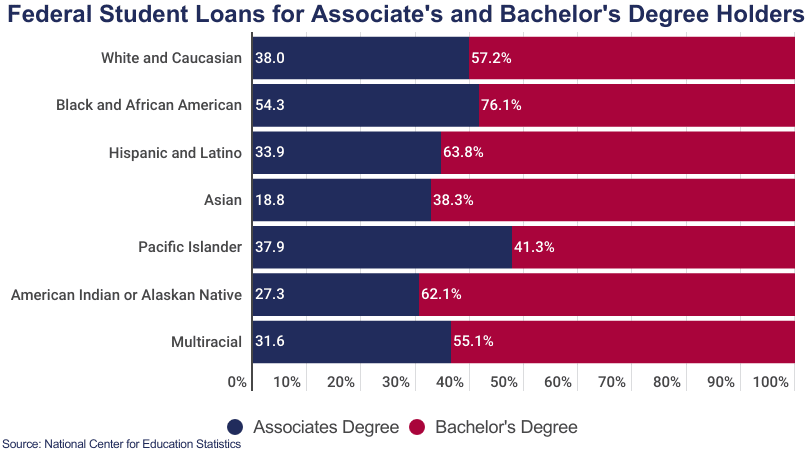
Demographic Disparities In Debt Levels
Student loan debt is a burden for many. It varies with age, race, and gender. This post explores these differences.
Gender Gap In Debt Ownership
Women carry more student debt than men. This gap is growing. Reports show women hold two-thirds of all student loan debt. The reasons are complex. Degree types and repayment challenges contribute to this trend.
Key Points:
- Women have higher debts after graduation.
- Economic factors make repayment harder for them.
Racial Divide In Student Loans
The debt level is not equal across different races. Black and Hispanic grads have more debt than White or Asian peers. Systemic issues are to blame.
Statistics show:
| Race | Average Debt |
| Black graduates | $52,726 |
| Hispanic graduates | $36,266 |
| White graduates | $28,006 |
| Asian graduates | $25,523 |
Income gaps and access to scholarships play roles. These issues need addressing.
Key Issues:
- Access to financial resources is unequal.
- Minority students face unique repayment challenges.
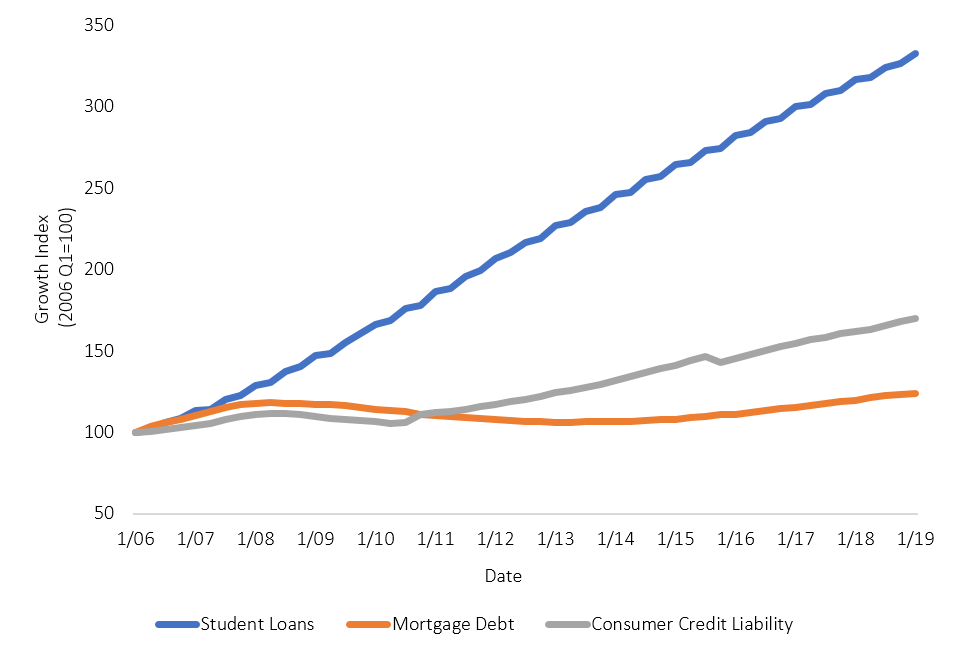
Consequences For The Economy
Millennial student loan debt casts a long shadow over the economy. Understanding its impact can reveal much about current financial trends and future market directions. Let’s explore how this debt influences various economic aspects.
Effect On Housing Market
Burdensome student loans are delaying homeownership for many millennials. High monthly payments reduce the ability to save for a down payment. This trend leads to a shift in housing demand, with more millennials opting to rent rather than buy. The following points outline the housing market effects:
- Increased demand for rental properties
- Lower home ownership rates among young adults
- Diminished new household formation
Implications For Consumer Spending
Millennials with significant student debt often have less disposable income. This limits their spending power, affecting various industries. Consumer spending trends illustrate key points:
| Category | Impact |
|---|---|
| Retail | Decreased frequency of purchases |
| Travel | Lower budget for vacations |
| Luxury Goods | Reduced expenditure |
Influence On Employment Choices
Debt levels might compel graduates to prioritize job security over passion or personal interest. This can lead to work in fields not aligned with their education or preferences. Below are some influences on employment:
- Preferring higher-paying jobs over potentially fulfilling but lower-paying careers
- Considering side gigs and freelance work to supplement income
- Avoiding entrepreneurial ventures due to financial risk
Government And Private Sector Responses
Tackling the burden of student loan debt requires action from all sides. Both the US government and the private sector have rolled out a series of initiatives. These efforts aim to lighten the load for millions of Americans grappling with student loans. They signal a critical step toward financial health for the millennial generation.
Federal Loan Forgiveness Programs
The government has introduced programs to help defray the cost of higher education. The most notable is Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF). This program benefits individuals who work in public service jobs. After making 120 qualifying payments, remaining debt gets forgiven.
Another program is the Teacher Loan Forgiveness Program. This supports those who teach in low-income schools. After five years of service, qualified teachers can have up to $17,500 of their loans forgiven.
Employer-assisted Repayment Benefits
The private sector is also stepping up to the plate. Employers now offer student loan repayment benefits. These benefits are part of competitive compensation packages to attract and retain talent. Companies such as Google, Aetna, and Fidelity contribute directly to employees’ loan repayments.
- Some employers match student loan payments
- Others provide one-time or recurring contributions
Such perks not only help employees reduce their debt faster. They also show a commitment to employee financial well-being.
Innovative Financial Solutions
Tech startups and financial institutions have developed tools to manage student loans. Refinancing platforms lower interest rates and consolidate loans. This results in more manageable monthly payments.
Online calculators help students plan their repayment schedules efficiently. Apps and websites offer personalized advice. They use complex algorithms to suggest the best repayment strategies.
Other creative solutions include:
- Income Share Agreements (ISAs)
- Crowdfunding for education costs
Credit: www.choicesmagazine.org
The Future Of Millennial Debt
Millennial debt continues to shape financial landscapes. With student loans as a massive chunk, this generation faces unique challenges. Understanding what lies ahead is vital.
How will millennial debt evolve? Key factors include economic fluctuations, policy changes, and personal finance behavior. This section explores the future through predictions and trends, potential education reform, and personal finance strategies for millennials.
Predictions And Trends
Student loan debt is a defining feature of millennial finances. Analysts forecast several trends.
- Debt growth: Expect debts to inflate as tuition rates climb.
- Government action: Policy shifts could alter repayment scenarios.
- Technology: Fintech innovations may offer new solutions.
The Role Of Education Reform
Education reform could turn the tide on debt statistics.
| Initiative | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Tuition-free programs | Could reduce the need for loans. |
| Loan forgiveness | May alleviate existing debt burdens. |
| Financial literacy | Empowers smarter borrowing and spending. |
Personal Finance Management For Millennials
Financial literacy and budgeting are critical skills.
- Budgeting tools: Track spending and plan for repayments.
- Emergency funds: Prepare for unforeseen expenses.
- Income-based repayments: Tailor payments to earning levels.

Credit: www.profgalloway.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Millennial Student Loan Debt Statistics
What Is The Average Millennial Student Loan Debt?
The average student loan debt for millennials stands at around $36,000. This reflects the rising costs of higher education and the financial challenges that this generation faces.
How Many Millennials Have Student Loan Debts?
Nearly 15 million millennials in the U. S. are burdened by student loan debts. This equates to approximately 1 in 3 individuals within this generational cohort carrying educational debts.
What Percentage Of Millennials Are Debt-free?
Only about 16% of millennials are completely debt-free, indicating that the vast majority of this age group is managing some form of debt, including student loans.
Are Millennial Student Loan Debts Increasing?
Yes, millennial student loan debts have been on the rise, largely due to escalating tuition fees and increased attendance at higher-cost institutions.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of student loan debt is a challenge for many millennials. The statistics we’ve explored reveal both the scale of this issue and its nuances. As this generation takes strides toward financial freedom, understanding these figures becomes crucial.
Let’s empower ourselves with knowledge to tackle debt head-on and move towards a more secure future.







