Canadian Millennials Student Debt: Solutions Unveiled

Canadian millennials face an average student debt exceeding $17,000, challenging their financial stability. The burden affects housing affordability and savings potential.
Navigating the financial landscape, Canadian millennials grapple with substantial student loan debts after graduation. This debt load not only hampers their ability to save for future investments but also significantly impacts their day-to-day budgeting and long-term economic well-being. As the cost of tertiary education continues to rise, the concern surrounding the ability of young Canadians to pursue higher education without accruing overwhelming debt grows.
The student debt issue resonates across demographics, influencing broader economic factors like the housing market, consumer spending, and the transition to adulthood milestones. Addressing this debt crisis is crucial for the financial health of individuals and the overall economic prosperity of the country.
Millennial Debt Crisis In Canada
The term Millennial Debt Crisis paints a troubling picture for young adults in Canada. It reflects a situation where loan balances swell and financial freedom seems a distant dream. Canadian Millennials face a unique set of challenges, bearing the weight of substantial student debt. Financial pressures mount as they pursue education and strive for a foothold in an ever-competitive job market.
In this deep dive, we dissect the scope of the debt iceberg many Millennials are silently chipping away at. Let’s explore this financial conundrum in detail.
Surveying The Scale Of Student Debt
Millennials in Canada are hitting milestones with a ball and chain of debt slowing their pace. Insights into the magnitude of student loans shed light on their fiscal health.
- Numbers don’t lie: A substantial fraction of Millennials grapple with five-figure debts.
- Getting higher education is often synonymous with accruing hefty loans.
- Repayment spans decades, trapping many in a cycle of interest and installments.
Comparing Past And Present: A Generational Debt Shift
The chasm between past and present financial realities for Canadian graduates is alarmingly deep.
| Generation | Average Debt at Graduation | Years to Repay |
|---|---|---|
| Boomers | $10,000 | 10 years |
| Generation X | $15,000 | 14 years |
| Millennials | $30,000 | 20+ years |
These numbers clear the fog, revealing a stark generational debt shift. Millennials face loan amounts triple those of Boomers, with double the repayment period.
Staying informed is key in navigating the financial hurdles ahead. The Millennial debt crisis underscores a larger societal shift, with ripple effects to come.

Credit: www.autonews.com
Root Causes Of Escalating Student Debts
Understanding why student debt is on the rise is crucial. Many factors play a role. Let’s explore these factors.
Rising Cost Of Post-secondary Education
Tuition fees are soaring. Students face higher costs than ever before. Expenses aren’t limited to classes alone.
- Textbooks and resources add up quickly.
- Living expenses, like housing, also contribute greatly to debt.
Financial aid has not kept pace with these rising costs. Students must find more money to cover them.
Changing Employment Landscape For Graduates
Graduates are entering a tough job market. Good jobs are hard to find. Many positions require experience not gained in school.
New graduates often settle for lower-paying jobs. These jobs make it hard to pay off loans quickly. The result is long-term debt.
The Psychological Impact On Canadian Millennials
Imagine struggling with a huge debt right after college. That’s the reality for many Canadian millennials. Student debt doesn’t just affect their finances. It reaches deep into their mental well-being. Let’s explore how.
Mental Health Challenges
Many millennials face mental health challenges due to student debt. Anxiety and depression cases have spiked. Here’s why:
- Constant worry over repaying loans
- Pressure to succeed quickly escalates
- Financial stress takes a toll on their mindset
This stress often leads to sleepless nights. Daily tasks become harder. Enjoying life seems like a distant dream.
Stress
Stress from debt is heavy. It’s like a weight on millennials’ shoulders. They feel it every day. Here are their stress triggers:
- Large monthly payments
- Fear of not finding high-paying jobs
- Lack of financial freedom
These worries can overshadow their hope for the future.
Delayed Life Milestones: Buying Homes, Starting Families
| Milestone | Impact of Debt |
|---|---|
| Buying Homes | Down payments feel impossible with student loans |
| Starting Families | Many delay having kids due to financial insecurity |
These delays can cause more than just temporary setbacks. They shape the future of an entire generation.

Credit: www.nytimes.com
Government Initiatives And Debt Relief Programs
The burden of student debt for Canadian millennials remains a pressing issue. Recognizing the challenge, various government initiatives and debt relief programs aim to ease the financial strain. These measures provide significant support, aiming to alleviate the pressures of repayments. Through federal and provincial interventions, as well as opportunities to reduce the need to borrow in the first place, students are finding new ways to manage their educational expenses.
Federal And Provincial Loan Relief Measures
The Canadian government offers numerous loan relief programs for post-secondary students. These initiatives help manage and repay student loans, providing much-needed support to millennials. The focus rests on making repayment terms manageable and providing relief based on income or life circumstances.
- Repayment Assistance Plan (RAP)
- Revision of Terms
- Loan Forgiveness for Doctors and Nurses
Provinces across Canada also have tailored programs designed to lighten the student debt load. These programs often complement federal options and address specific regional needs.
Grants And Scholarships: Reducing The Need To Borrow
Grants and scholarships significantly decrease the necessity for students to rely on loans. These forms of financial aid do not require repayment, making them integral in managing student debt levels for millennials. Both federal and provincial governments, along with private organizations, offer these awards based on various criteria including:
- Merit-based scholarships
- Need-based grants
- Specific demographics or fields of study
By maximizing the use of grants and scholarships, students can significantly reduce the amount they need to borrow. This proactive approach paves the way for a future with a lighter financial burden.
Alternative Financing Models For Education
Millennials in Canada face a tough challenge with student debt. Traditional loans weigh heavy on young shoulders. Yet, the landscape is changing. Alternative Financing Models for Education are emerging. These new strategies offer creative solutions to fund academic pursuits without the burden of conventional debt structures.
Income Share Agreements: Pay-as-you-earn Schemes
Income Share Agreements (ISAs) offer breathing room for graduates. Under an ISA, students commit a future portion of their income to paying for their education. It’s a flexible path, enabling payment when graduates secure employment and their earnings reach a set threshold. ISAs are gaining popularity due to their fair and adaptable nature, adjusting payments based on actual income levels.
Crowdfunding And Community Support Initiatives
Crowdfunding harnesses the power of community to finance education. Websites like GoFundMe allow students to raise funds through small contributions from a large number of people. This approach not only eases the financial strain on students but also involves the community in supporting their educational journey. From small local scholarships to larger funding campaigns, crowdfunding makes education a collective goal.
Taking Control: Strategies For Millennial Debt Management
Millennials in Canada are increasingly feeling the weight of student debt. It can feel like a relentless burden. Yet, managing this debt effectively is crucial for financial well-being and peace of mind. The key is to take control and approach this challenge with proactive strategies. There are tried-and-true methods to navigate these waters and keep debt from overshadowing the future.
Financial Literacy And Personal Budgeting
Understanding money is the first step.
- Educate yourself on financial basics.
- Use budgeting tools to track spending.
- Identify essential expenses versus wants.
- Set goals to pay off debt faster.
Create a monthly budget plan. This includes:
- Total income from all sources.
- Fixed costs like rent and utilities.
- Variable expenses such as groceries and entertainment.
- Student loan payments.
Sticking to your budget is vital. This helps you spend wisely and save more.
Debt Consolidation And Refinancing Options
Multiple loans can be overwhelming.
- Debt consolidation can simplify payments.
- Look for options with lower interest rates.
- Consider longer repayment terms to reduce monthly costs.
- Refinancing might result in substantial savings over time.
Review your existing loans. Then:
- Gather loan details like balance and interest rate.
- Research available consolidation and refinancing options.
- Compare terms and decide on the best plan.
- Contact financial institutions to apply.
Consolidating or refinancing can be a powerful move. It helps manage payments and reduces financial stress.
The Road Ahead: Policy Recommendations
Millennials in Canada face a unique challenge: managing their education costs and the burden of student debt. As we look to the future, proactive policies can pave the way for financial relief and sustainable education systems. The next sections highlight crucial policy recommendations to reshape the landscape of student financing for Canadian millennials.
Reforming Student Loan Systems
Change starts with reform in student loan systems. Key areas include:
- Interest rates: Lowering or removing these can ease the burden.
- Repayment terms: Flexibility in repayment can prevent defaults.
- Forgiveness programs: These encourage timely completion of studies.
Opportunities also lie in income-driven repayment plans and loan refinancing options. Both can turn impossible debt into manageable commitments.
Investing In Affordable And Accessible Education
A focus on accessibility and affordability shapes a better future.
- Grants over loans: This shifts the emphasis on non-repayable aid.
- Subsidized tuition: Allows students from all backgrounds to enroll.
- Online education options: These offer flexible, lower-cost alternatives.
Further, partnerships with industry can create co-op programs and internships. They provide both experience and funding for students.
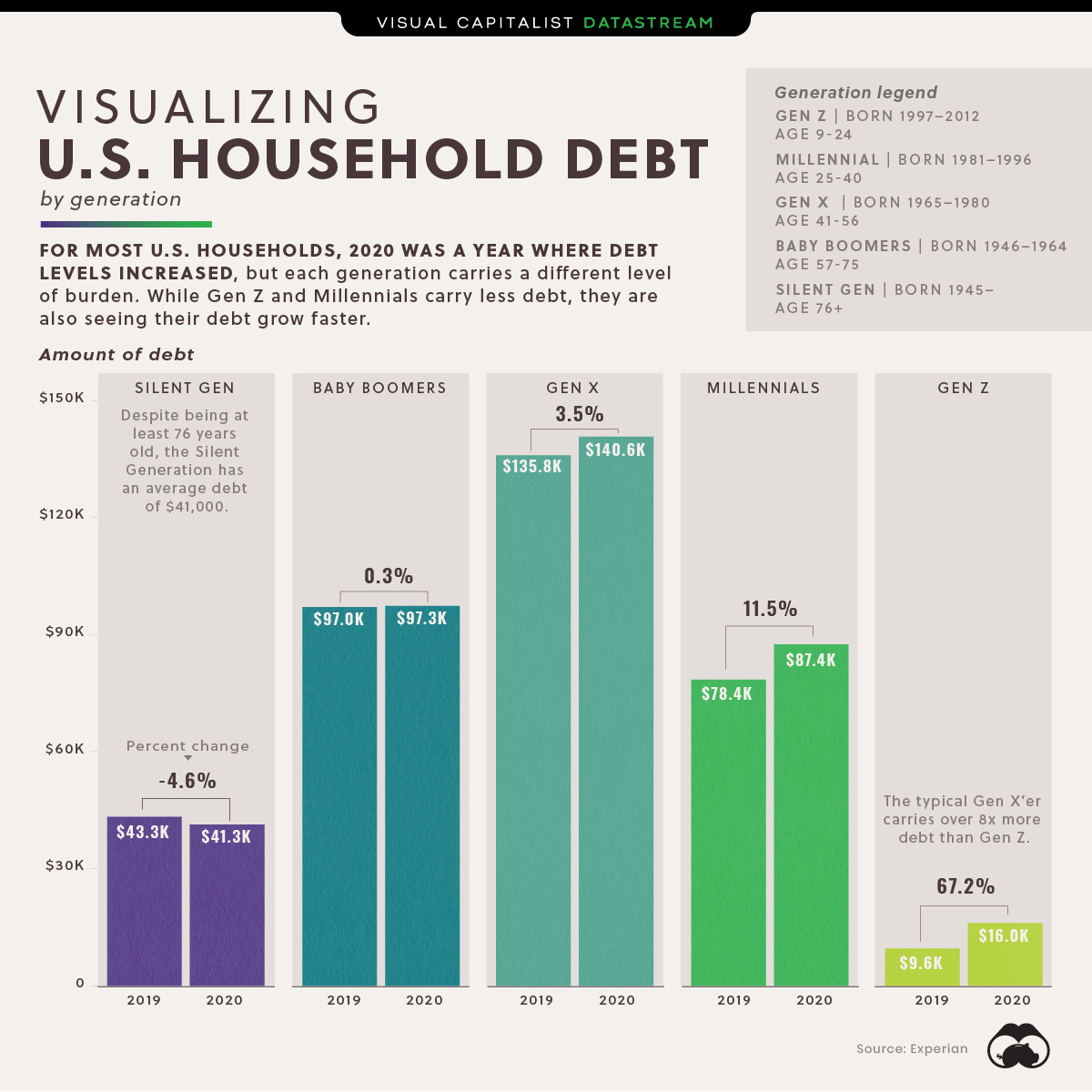
Credit: www.visualcapitalist.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Canadian Millennials Student Debt
What Is The Average Student Debt In Canada?
The average student debt for Canadian millennials is approximately $17,500 upon graduation. This figure varies by province and type of institution attended.
How Long Does Paying Off Student Loans Take?
On average, Canadian millennials may take up to 10 years to fully pay off their student loans. Repayment duration can differ based on income, loan amount, and repayment plan chosen.
Are Student Loans Impacting Millennials’ Home Ownership?
Yes, the burden of student loans is significantly delaying home ownership for many Canadian millennials. High debt levels can limit saving for down payments and affect mortgage qualifications.
Can Student Debt Be Forgiven In Canada?
In certain circumstances, such as insolvency or severe financial hardship, Canadians may apply for the Repayment Assistance Plan or consider loan forgiveness options, though these are limited and have specific eligibility criteria.
Conclusion
Navigating student debt is a defining challenge for Canadian millennials. This post has shared insights to help tackle these financial burdens. Sound strategies and informed decisions will pave the way forward. Let’s commit to empowering this generation toward a debt-free future.
Your financial freedom awaits.







